First introduced in the 1960’s, photo etching has rapidly progressed with its capabilities and advantages growing by the year.
Referred to by engineers and designers by many names, including chemical milling, chemical machining, photochemical milling, photo etching, photochemical machining, and chemical etching, Photochemical Etching (PCE) has become a popular choice due to its high-precision, fast-turnaround and cost-effectiveness. But, what exactly is chemical etching?
In this article, we take a deep dive into photochemical etching, looking at its process, applications and benefits so you know exactly when to use it and most importantly: why.
What is chemical etching?
Also known as photochemical machining (PCM) and chemical blanking, photochemical etching is a highly precise, cost-effective metal machining process used to produce complex components from various metals.
An ideal process for precision thin metal parts, the process allows the delivery of parts with complex or intricate geometries and tight tolerances for various industries, including telecommunications, defense, medical, and electronics.
This type of etching uses photo-sensitive material to transfer part images onto metal sheets before a chemical etchant is used to dissolve the unwanted sections.
Photochemical etching is ideal for thin metal parts and features minimal surface burrs and imperfections.
What is the chemical etching process?
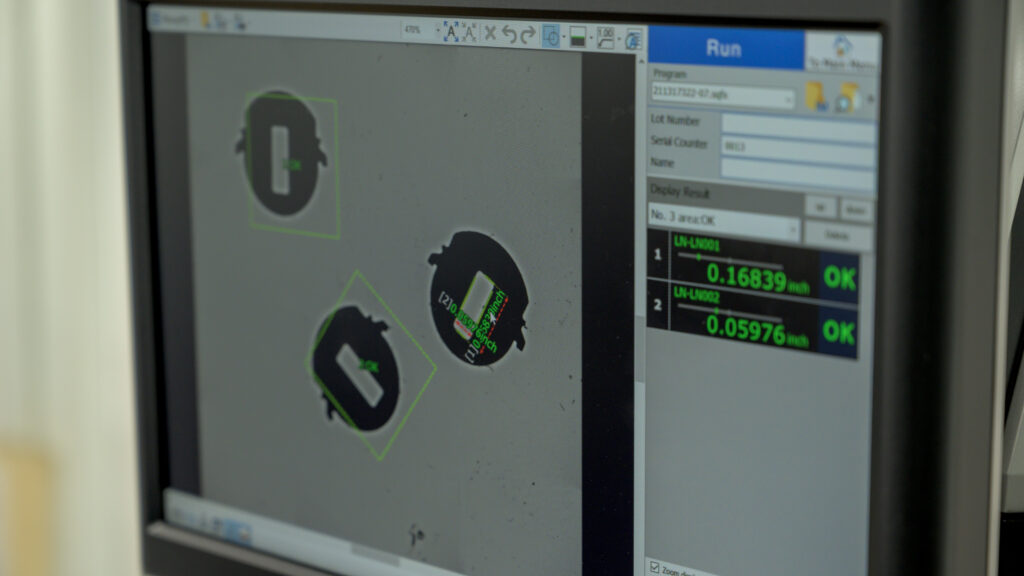
Etching is a multi-step process with many moving parts. While the chemical etching process may appear complex at first glance, it is fast, affordable and precise, making it an excellent choice for metal prototyping and production. At E-Fab, our proven process ensures the delivery of precision thin metal parts.
Each step of the PCE process is exact and designed to produce highly accurate parts.
The chemical etching process:
Step One
CAD technology creates a digitally rendered design of a part (known as a Phototool).
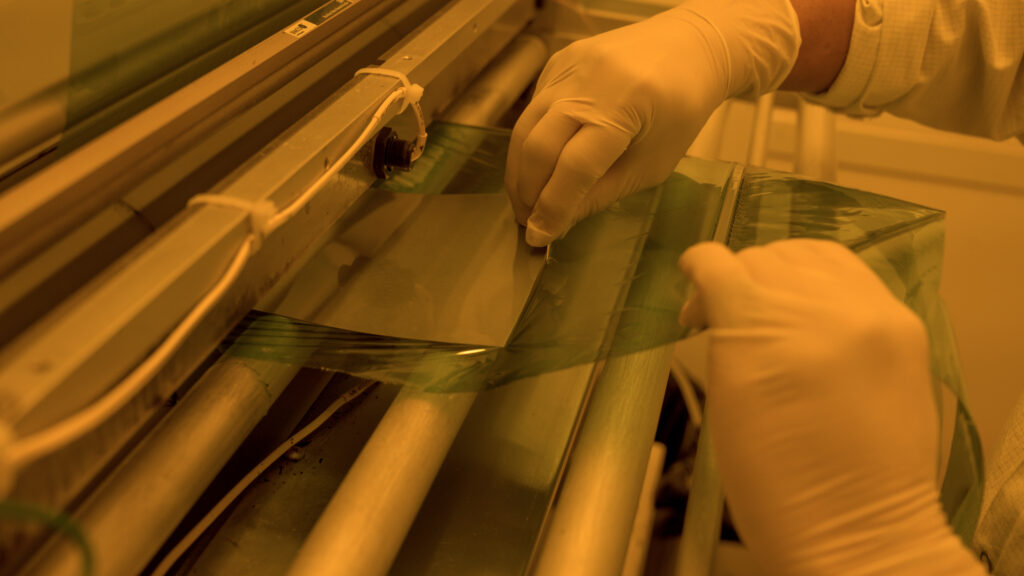
Step Two
Coat both sides of a metal sheet with a polymer (called a Photoresist) that’s UV light sensitive and acid resistant and vacuum seal that sheet.
Step Three
Expose the Phototool onto the Photoresist using UV lamps.
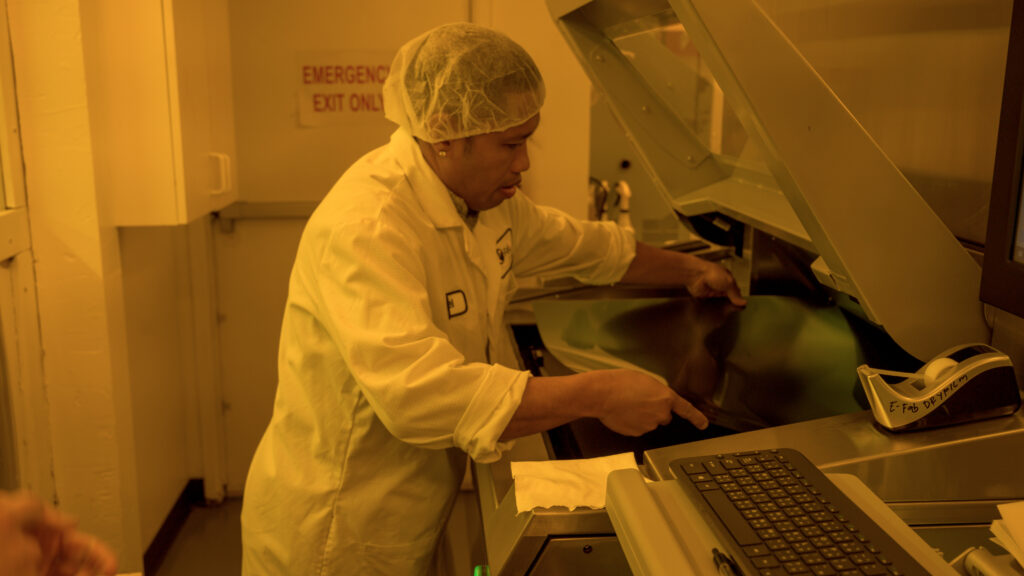


Step Four
The unexposed coating is washed away by a developing solution, leaving a mask of the part.
Step Five
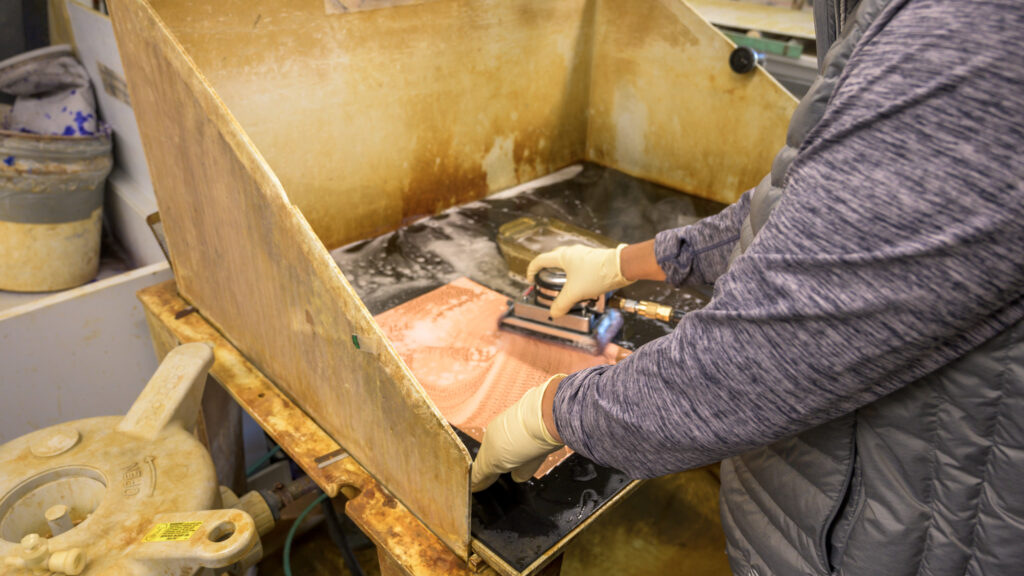
An etching machine sprays a chemical etchant on the sheet, leaving the designed part.
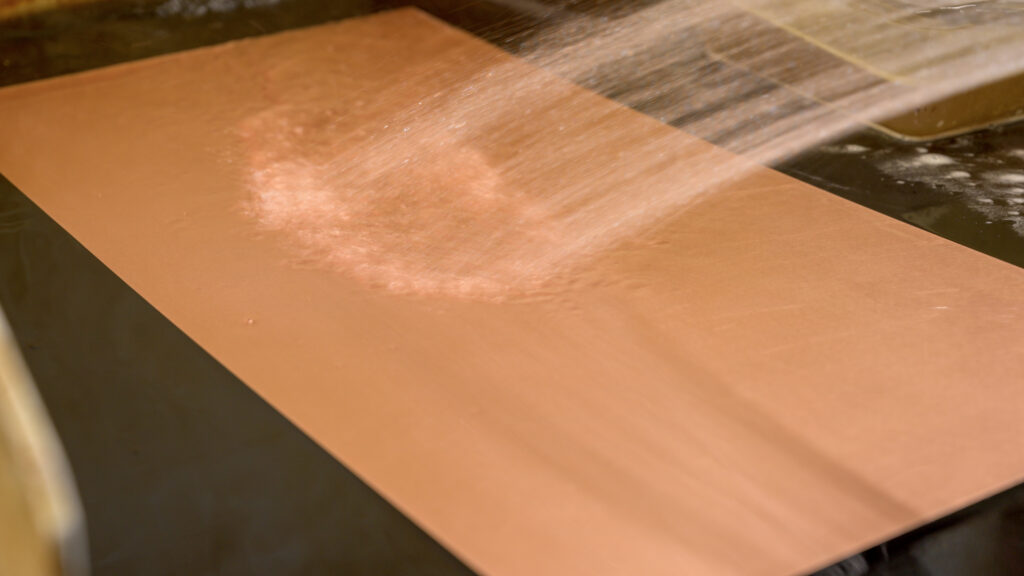
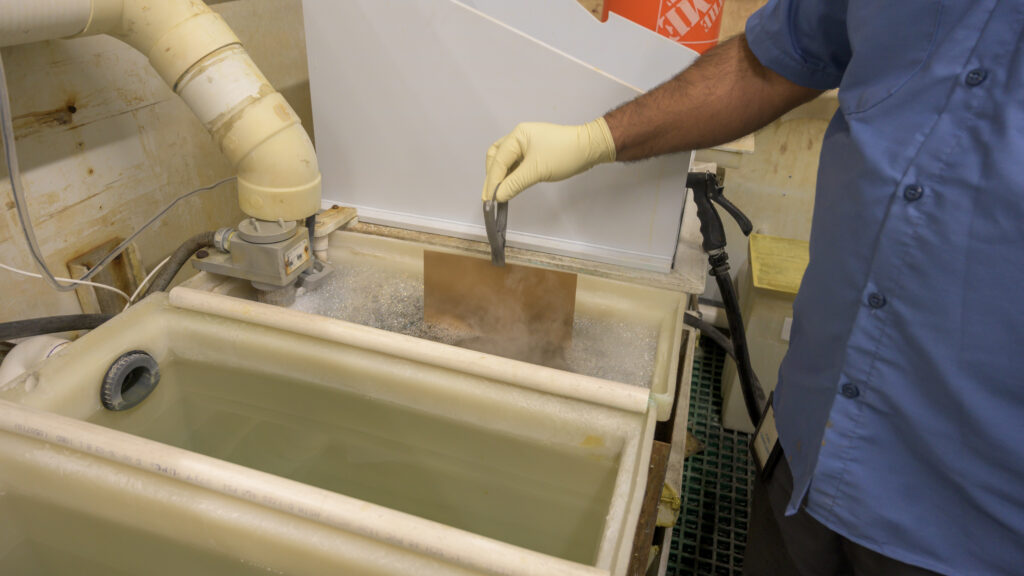


Step Six
An alkaline solution removes the mask from the metal surface.
Step Seven
Each part is formed into three-dimensional shapes as requested.
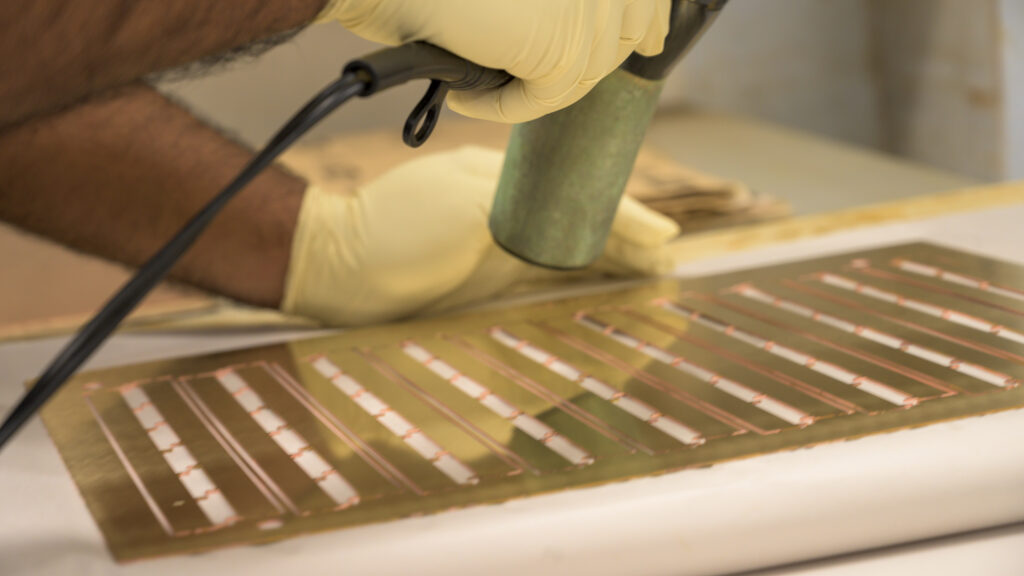
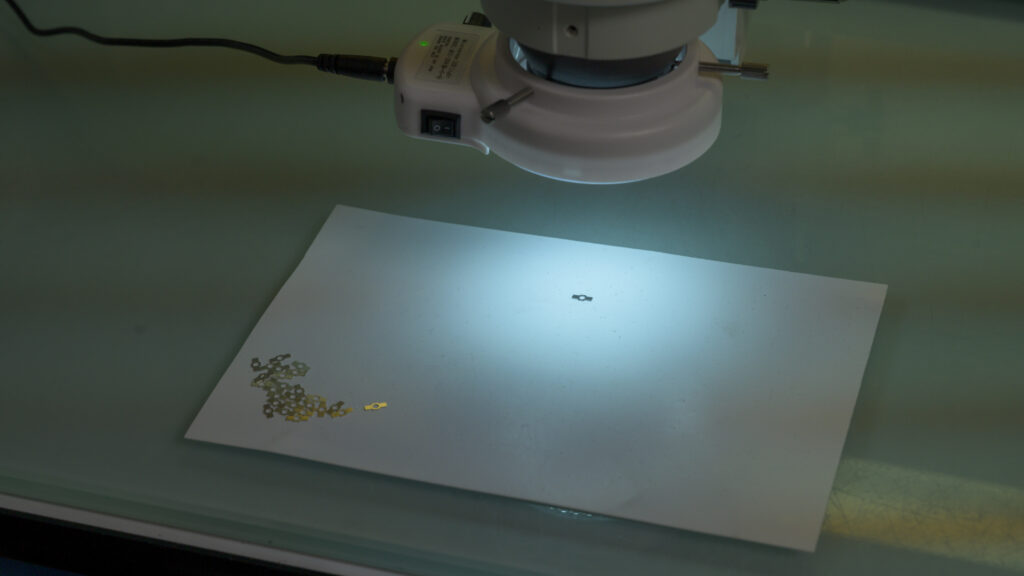


Step Eight
Highly calibrated technology inspects every part for accuracy, precision, and quality.
The Main benefits of the chemical etching process include:
-
- Inexpensive tooling
-
- Fast prototyping
-
- Low tolerances maintained with precision
-
- Burr and stress free
-
- Complex designs
What are the best applications for chemical etching?
Due to its speed, affordability and precision, chemical etching is the ideal process for components in a number of industries. These include:
-
- Automotive
-
- Aerospace
-
- Medical
-
- Electronics
-
- RF microwave
-
- Energy
Perfect for metals that are often challenging to profile using conventional sheet metalworking, chemical etching is perfect for producing a wide range of aerospace components.
This can include everything from heat exchanger plates for use in aircraft dehumidifiers and engines to contacts and connectors.
E-Fab produces dozens of parts utilizing PCE, including meshes, circuits, grids, shields, and electrodes for leaders in the aerospace, energy, telecommunications, microwave, and semiconductor industries.
The Benefits of Chemical Etching
The photochemical etching process’s affordability, speed and precision offer enormous benefits for large production and quick prototyping of metal parts. And, the benefits go a lot deeper than that.
1. Fast Turnaround and Production
The digital nature of photochemical etching part designs allows for faster production of prototypes and production-quality pieces. Design engineers can easily modify the part design using computer software without needing new tooling.
Because the photochemical etching process begins on a computer, parts can be produced more quickly, with no retooling costs or delays if a change is required.
When compared to mechanical machining operations, photochemical etching operations have lower tooling costs because they use chemical etchants and digitally rendered designs to produce a finished part.
Furthermore, the process accommodates part designs with greater complexity or tighter tolerances without significantly increasing production costs.
2. High precision
The photochemical etching process enables high-precision machining. By contrast to conventional machining techniques like stamping and laser cutting, chemical etching does not affect metal’s hardness, grain structure, or ductility.
With chemical etching you get:
-
- Precise, uniform parts
-
- Easy production of fine details and complex geometries
-
- Micro precision controlled process for multidimensional etching
-
- Production of unconventional designs
-
- Tight tolerances
3. Cost-Effective Production
Compared to other machining methods, photochemical etching is the more affordable choice. Unlike mechanical machining, which requires manual design, digitally drawn designs and chemical etchants result in lower tooling costs throughout production.
A phototool can be made quickly, can last the part’s life (if not longer), and can be reproducible, allowing for large production runs at reduced costs. This results in:
-
- Thousands of dollars saved compared to hard tooling methods
-
- A price not based on geometry
-
- The affordable production of complex and intricate parts
-
- The ability for low-cost, late design changes
-
- Prototype to production using the same process
Photochemical etching: the cost-effective alternative
One of the main reasons why photochemical etching has become so popular is due to its cost-effectiveness as an alternative to other metal fabrication methods.
The fact is, when compared to other machining processes, photochemical etching definitely comes out as more affordable.
One of the main reasons is tooling. Unlike costly conventional methods such as stamping, photo etching tooling is digital. Using chemical etchants and digitally produced designs to create a final item, tooling costs are low compared to mechanical machining operations.
Digital tooling also allows for easy and late modifications to designs which can significantly reduce the overall project time, saving valuable time and money.
Read our article for even more reasons to use photochemical etching.
A proven partner for photochemical etching
If you’re looking for a reliable partner for your photochemical etching, the team at E-Fab are here to help. We’ve been using photochemical etching since our beginnings, producing thin metal parts in various materials for the telecommunications, defense, medical, and electronics industries.
E-Fab uses industry-leading equipment to turn various metal and composite materials into parts for various industries using photochemical etching and various wet machining technologies.
Our innovative processes and expert staff ensure that every component we fabricate is of the highest quality.
Our areas of expertise include:
-
- Design/engineering assistance
-
- Material selection
- Metrology
-
- CNC machining (including micromachining)
-
- Lamination
-
- Heat treating
-
- Electro and electroless plating
-
- Joining (including welding, wire bonding, soldering, and braising)
- Bonding
- Black Oxide
- Forming
Learn more about our photochemical etching services today.

